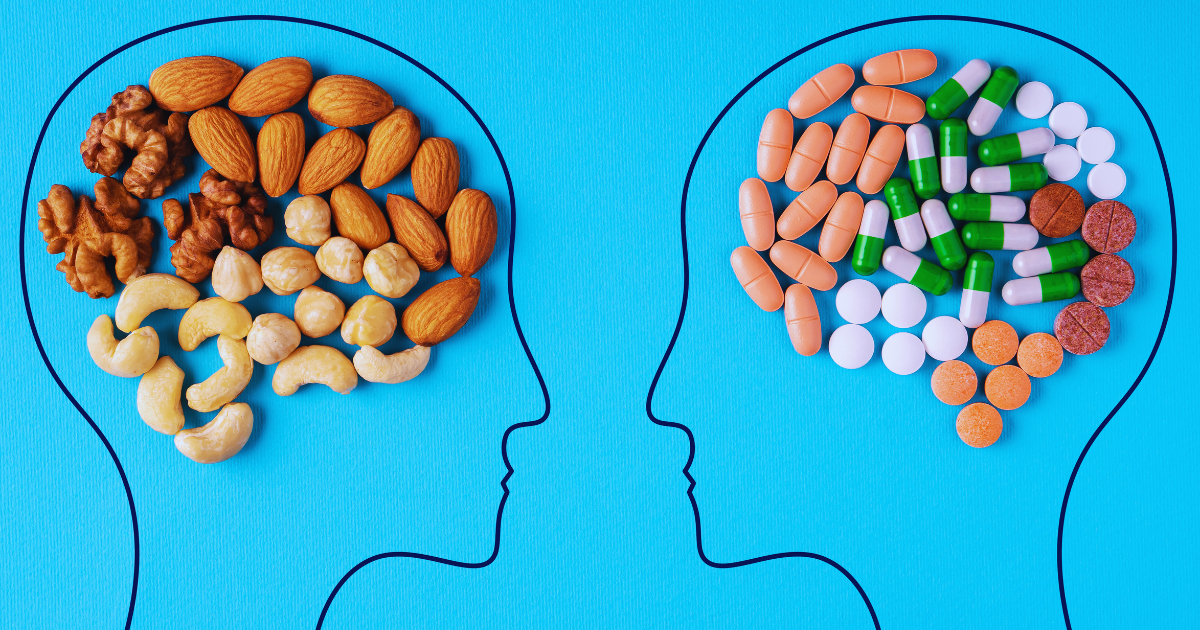
The connection between our gut and brain, often called the gut-brain axis, is a complex and vital relationship that significantly influences our overall well-being.
This intricate communication network links the brain’s emotional and cognitive centers with peripheral intestinal functions. Our diet profoundly impacts this relationship, suggesting that what we eat not only fuels our bodies but also affects our mental health.
Understanding this connection is crucial, as it opens new avenues for managing mental health through dietary choices, emphasizing the importance of nutrition in mental wellness.
The Connection Between Diet and Mental State
Our dietary choices, influenced by the gut-brain axis, significantly affect our mental health. Processed foods high in sugar and additives can disrupt our gut microbiome, leading to inflammation and negatively impacting brain health, potentially causing mood swings and anxiety.
Conversely, a diet rich in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and grains supports a healthy microbiome, promoting serotonin production for mood regulation. Essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids in fatty fish and flaxseeds, antioxidants in berries and greens, and probiotics in yogurt and fermented foods play key roles in enhancing mental well-being by reducing anxiety and protecting brain cells.
By prioritizing these nutrient-dense foods, we not only nourish our bodies but also fortify our mental health. In doing so, it’s essential to remember the broader picture of wellness, including how we manage healthcare costs. Smartly utilizing resources like pharmacy discounts for necessary supplements or medications can ensure comprehensive care, seamlessly integrating physical and mental health support.
Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Mental Health

Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria found in certain foods and supplements, whereas prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed these good bacteria, helping them to flourish in the gut. Together, they play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy microbiome linked to improved mental health through the gut-brain axis.
A balanced microbiome can reduce inflammation and regulate mood-enhancing neurotransmitters, thus potentially easing symptoms of depression and anxiety. To incorporate probiotics into your diet, consider yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kombucha, which are rich in live cultures.
For prebiotics, focus on foods like bananas, onions, garlic, and asparagus, which provide the necessary fiber to support healthy gut flora. You can foster a gut environment conducive to mental well-being by consciously including probiotics and prebiotics in your meals.
Foods to Embrace for a Healthier Mind
To foster a healthier mind through diet, consider these five categories of foods known for their positive impact on gut health:
- Fermented Foods – Including yogurt, kefir, kombucha, and sauerkraut in your diet can introduce beneficial probiotics to your gut, enhancing both digestive and mental health. These foods help maintain a balanced microbiome, which is crucial for optimal brain function and mood regulation.
- Omega-3 Rich Foods – Foods like salmon, chia seeds, and walnuts are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been linked to decreased levels of anxiety and depression. Omega-3s play a crucial role in brain health, reducing inflammation and supporting cognitive functions.
- High-Fiber Foods – Consuming various fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the necessary fiber to nourish beneficial gut bacteria. These high-fiber foods help produce short-chain fatty acids, which have protective effects on the brain.
- Lean Proteins – Sources of lean protein such as chicken, fish, and legumes are essential for synthesizing neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, significantly influencing mood and mental well-being.
- Polyphenol-Rich Foods – Foods high in polyphenols, such as blueberries, strawberries, and nuts (especially almonds and pistachios), can also contribute to a healthy gut microbiome. Polyphenols have antioxidant properties that support brain health by reducing oxidative stress.
Foods to Avoid or Limit
Foods that can negatively impact gut health and mental well-being include those high in sugar, artificial sweeteners, and heavily processed items. These foods can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome, leading to inflammation and a decrease in the production of mood-regulating neurotransmitters.
High sugar intake is associated with fluctuations in blood glucose levels, contributing to mood swings and increased anxiety. Artificial sweeteners may negatively affect gut bacteria, while processed foods often contain unhealthy fats and additives that can exacerbate mental health issues.
Moreover, foods high in trans fats, such as fried foods, certain baked goods, and some margarine, should be consumed cautiously. Trans fats contribute to systemic inflammation, which has been linked to an increased risk of depression.
To reduce consumption of these foods, focus on whole, nutrient-dense options and read labels carefully to avoid hidden sugars and additives. Gradually decreasing your intake of sweetened beverages, opting for natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup in moderation, and preparing meals from scratch can help limit exposure to these detrimental ingredients, supporting gut health and overall mental well-being.
Conclusion
Embracing a balanced diet is a decisive step in caring for your mental health. Remember, achieving optimal mental well-being goes beyond just one factor—it’s a complex interplay of lifestyle choices, including nutrition. By integrating thoughtful dietary habits, you contribute to a holistic approach that supports not just mental but overall fitness. Let your diet be a cornerstone of your journey towards good health.
Shawn is a passionate coach who empowers individuals to achieve their goals and reach new heights of success. With his experience in the personal development industry, Shawn has guided countless people towards fulfilling their potential and achieving outstanding results in life. He has experience in the personal development industry for more than 7 years and has helped countless success seekers to achieve outstanding success in life. Learn more about him on Everydaypower.com or Goalcast.com